TD Vaccine Names

The diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTP) vaccine, also known as the TD vaccine, is a crucial immunization that protects against three serious bacterial infections: diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough). The vaccine is typically administered in a combination format, with various vaccine names depending on the specific formulation and the target age group. Understanding the different vaccine names and their components is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to navigate the complex landscape of immunizations.
Overview of TD Vaccine Names
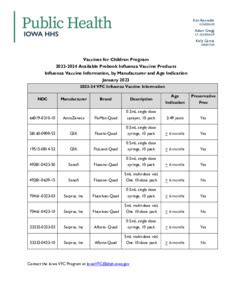
The TD vaccine is available in several formulations, each with its own set of vaccine names. The most common formulations include:
- Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids (DT) vaccine, which protects against diphtheria and tetanus
- Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTP) vaccine, which protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis
- Tetanus and Diphtheria Toxoids (Td) vaccine, which protects against tetanus and diphtheria
- Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis (Tdap) vaccine, which protects against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis
Specific Vaccine Names and Formulations
Some of the specific vaccine names and formulations include:
| Vaccine Name | Formulation |
|---|---|
| DTaP (Daptacel) | Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis vaccine |
| DTaP (Infanrix) | Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis vaccine |
| Td (Decavac) | Tetanus and Diphtheria Toxoids vaccine |
| Tdap (Adacel) | Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis vaccine |
| Tdap (Boostrix) | Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis vaccine |
Key Considerations for Vaccine Administration

When administering the TD vaccine, healthcare professionals should consider several key factors, including:
- Age and risk factors: The TD vaccine is typically administered to individuals of all ages, with specific formulations recommended for different age groups.
- Contraindications and precautions: Certain individuals may be contraindicated or require precautions when receiving the TD vaccine, such as those with a history of severe allergic reactions or neurological disorders.
- Booster doses: Booster doses of the TD vaccine are typically recommended every 10 years to maintain immunity against tetanus and diphtheria.
Key Points
- The TD vaccine is available in several formulations, including DT, DTP, Td, and Tdap.
- Specific vaccine names and formulations may vary depending on the country, region, or manufacturer.
- Healthcare professionals should consult relevant vaccine package inserts and guidelines for specific information on vaccine administration and dosage.
- Age and risk factors, contraindications and precautions, and booster doses are essential considerations for vaccine administration.
- Understanding the different vaccine names and formulations is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of immunizations.
Future Directions and Implications
As the landscape of immunizations continues to evolve, it’s essential to stay informed about the latest developments and recommendations. Future directions may include the development of new vaccine formulations, updates to existing guidelines, and changes in vaccine administration practices. By staying up-to-date on the latest information and guidelines, healthcare professionals can provide the best possible care for their patients and help protect against serious bacterial infections.
What is the difference between the DT and Td vaccines?
+The DT vaccine protects against diphtheria and tetanus, while the Td vaccine protects against tetanus and diphtheria. The Td vaccine is typically used as a booster dose for adults and adolescents, while the DT vaccine is used for primary immunization in children.
Can I receive the TD vaccine if I have a history of severe allergic reactions?
+Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions should consult their healthcare provider before receiving the TD vaccine. In some cases, precautions or alternative formulations may be recommended.
How often do I need to receive booster doses of the TD vaccine?
+Booster doses of the TD vaccine are typically recommended every 10 years to maintain immunity against tetanus and diphtheria. However, specific recommendations may vary depending on age, risk factors, and other considerations.



