Social Vs Cultural Determinants Of Health

The concept of health is multifaceted, influenced by a wide range of factors that extend beyond the individual to encompass societal and cultural dimensions. The social and cultural determinants of health are particularly significant, as they shape the environments in which people live, work, and interact, ultimately affecting their well-being and health outcomes. Understanding the distinction between social and cultural determinants is crucial for developing effective public health interventions and policies that address the root causes of health disparities.
Social determinants of health refer to the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age, including factors such as socioeconomic status, education, employment, housing, and access to healthcare services. These determinants are shaped by the distribution of money, power, and resources at global, national, and local levels. For instance, individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face challenges in accessing healthy foods, safe living environments, and quality healthcare, which can increase their risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of addressing social determinants to reduce health inequities and promote health for all.
Key Points
- The social determinants of health include socioeconomic status, education, employment, housing, and access to healthcare services.
- Cultural determinants of health encompass values, beliefs, and practices that influence health behaviors and outcomes.
- Understanding the interplay between social and cultural determinants is crucial for developing effective public health interventions.
- Addressing health disparities requires a comprehensive approach that considers the social, cultural, and economic contexts of individuals and communities.
- Policy interventions aimed at reducing health inequities should focus on creating equitable access to resources, services, and opportunities.
Social Determinants: A Deeper Dive

Social determinants are often categorized into several key areas, including economic stability, education, social and community context, health and healthcare, and neighborhood and environment. Economic stability, for example, is closely linked to health outcomes, as individuals with higher incomes tend to have better access to healthy foods, safe housing, and quality healthcare. Education is another critical determinant, as it empowers individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed health decisions and navigate complex healthcare systems.
Education as a Social Determinant
Education plays a pivotal role in shaping health outcomes, as it influences an individual’s ability to understand health information, adopt healthy behaviors, and access healthcare services. Higher levels of education are associated with better health literacy, which enables individuals to navigate healthcare systems more effectively, manage chronic conditions, and engage in preventive care. Furthermore, education can enhance socioeconomic status, leading to improved access to resources and opportunities that support health and well-being.
| Education Level | Health Literacy | Health Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Education | Improved Health Literacy | Better Health Outcomes |
| Lower Education | Poorer Health Literacy | Poorer Health Outcomes |

Cultural Determinants of Health
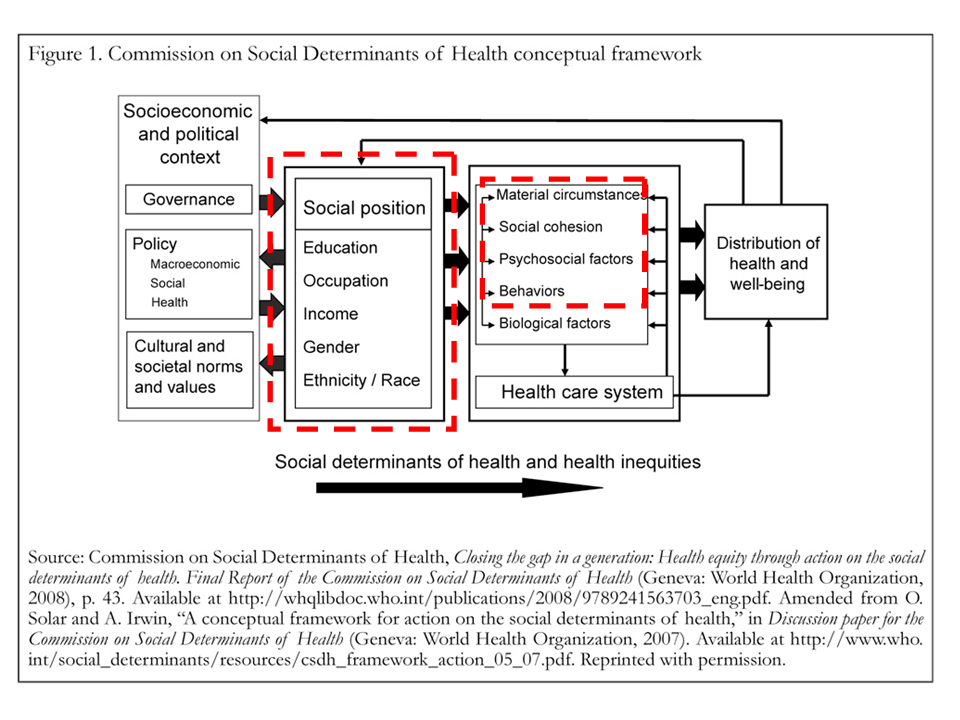
Cultural determinants of health, on the other hand, encompass the values, beliefs, and practices that influence health behaviors and outcomes. Culture can affect how individuals perceive health and illness, their beliefs about the causes of diseases, and their preferences for healthcare services. For example, in some cultures, traditional healing practices are preferred over conventional Western medicine, which can impact health outcomes if these practices are not evidence-based or if they delay seeking necessary medical care.
Cultural Competence in Healthcare
Cultural competence in healthcare is essential for providing effective care that meets the diverse needs of populations. Healthcare providers should be aware of the cultural beliefs and practices of their patients and adapt their care accordingly. This includes communicating effectively, respecting patient preferences, and incorporating traditional practices into care plans when appropriate. Cultural competence can improve patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment, and ultimately, health outcomes.
The interplay between social and cultural determinants of health is complex and bidirectional. Social determinants can influence cultural beliefs and practices, and vice versa. For instance, socioeconomic status can affect access to cultural resources and opportunities, which in turn can influence health behaviors and outcomes. Understanding this interplay is crucial for developing public health interventions that are culturally sensitive and socially relevant.
What are the primary social determinants of health?
+The primary social determinants of health include socioeconomic status, education, employment, housing, and access to healthcare services.
How do cultural determinants influence health outcomes?
+Cultural determinants influence health outcomes by shaping beliefs about health and illness, preferences for healthcare services, and adherence to treatment plans.
Why is cultural competence in healthcare important?
+Cultural competence in healthcare is important because it improves patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment, and health outcomes by respecting and incorporating patient preferences and cultural beliefs into care plans.
In conclusion, addressing the social and cultural determinants of health is essential for promoting health equity and reducing health disparities. Public health interventions and policies should be designed with a deep understanding of these determinants and their interplay. By acknowledging the complex social and cultural contexts in which health is shaped, we can work towards creating healthier environments and opportunities for all, ultimately improving health outcomes and well-being.



