Montana Access To Health

Montana, known for its vast landscapes and rural communities, faces unique challenges in providing access to healthcare for its residents. The state's geography, with its sprawling rural areas and limited access to specialized medical facilities, poses significant barriers to healthcare access. Despite these challenges, Montana has made significant strides in recent years to improve healthcare access, particularly through the expansion of Medicaid and the implementation of innovative healthcare delivery models. This article will explore the current state of healthcare access in Montana, highlighting both the challenges and the opportunities for improvement.
Key Points
- Montana's rural geography presents significant challenges to healthcare access, with many residents facing long distances to reach medical facilities.
- The expansion of Medicaid in Montana has increased healthcare coverage for low-income residents, but disparities in access to care persist.
- Innovative healthcare delivery models, such as telehealth and community health worker programs, are being implemented to improve access to care in rural areas.
- Addressing healthcare workforce shortages and improving health disparities are critical to ensuring equitable access to healthcare in Montana.
- Policy initiatives and community-based programs are essential for promoting healthcare access and addressing the unique needs of Montana's rural communities.
Healthcare Access Challenges in Montana

Montana’s rural geography is a significant factor in the state’s healthcare access challenges. Many residents face long distances to reach medical facilities, and the lack of public transportation options can further exacerbate these barriers. According to data from the United States Department of Agriculture, approximately 40% of Montana’s population lives in rural areas, which are often characterized by limited access to healthcare services. The rural-urban health disparities in Montana are particularly pronounced, with rural residents experiencing higher rates of chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease, compared to their urban counterparts.
Rural Healthcare Workforce Shortages
The shortage of healthcare professionals in rural Montana is another significant challenge to healthcare access. The state faces shortages of primary care physicians, dentists, and mental health professionals, which can lead to delayed or foregone care for rural residents. According to the National Rural Health Association, Montana has one of the lowest ratios of primary care physicians to population in the country, with only 64.6 primary care physicians per 100,000 people. This shortage is particularly concerning, given the critical role that primary care plays in preventing and managing chronic diseases.
| Healthcare Profession | Shortage Ratio |
|---|---|
| Primary Care Physicians | 64.6 per 100,000 people |
| Dentists | 42.1 per 100,000 people |
| Mental Health Professionals | 26.5 per 100,000 people |

Innovative Healthcare Delivery Models
Despite the challenges, Montana has made significant progress in implementing innovative healthcare delivery models to improve access to care. Telehealth programs, which use technology to deliver healthcare services remotely, have been particularly effective in increasing access to care for rural residents. According to data from the Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services, the number of telehealth visits in Montana increased by over 50% between 2018 and 2020. Additionally, community health worker programs have been implemented to provide outreach and support services to rural residents, helping to address social determinants of health and promote health equity.
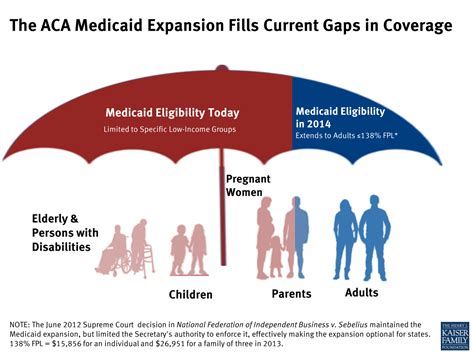
Medicaid Expansion and Healthcare Access
The expansion of Medicaid in Montana has also played a critical role in increasing healthcare access for low-income residents. According to data from the Kaiser Family Foundation, the Medicaid expansion has resulted in a significant reduction in the number of uninsured individuals in Montana, from approximately 13% in 2013 to 7% in 2020. However, disparities in access to care persist, with rural residents facing greater barriers to care compared to their urban counterparts. Addressing these disparities will require targeted policy initiatives and community-based programs to promote healthcare access and address the unique needs of Montana’s rural communities.
What is the current status of healthcare access in Montana?
+Montana faces significant challenges in providing access to healthcare, particularly in rural areas. Despite these challenges, the state has made progress in expanding Medicaid and implementing innovative healthcare delivery models to improve access to care.
How can telehealth programs improve healthcare access in rural Montana?
+Telehealth programs can help mitigate the effects of healthcare workforce shortages in rural Montana by leveraging technology to deliver healthcare services remotely. This can increase access to care for rural residents and reduce the need for in-person visits.
What policy initiatives can promote healthcare access in Montana?
+Policy initiatives such as increasing funding for community health worker programs, expanding Medicaid, and promoting telehealth programs can help promote healthcare access in Montana. Additionally, addressing healthcare workforce shortages and improving health disparities are critical to ensuring equitable access to healthcare in the state.
In conclusion, Montana’s unique geography and healthcare workforce shortages present significant challenges to healthcare access. However, the state has made progress in implementing innovative healthcare delivery models and expanding Medicaid to improve access to care. Addressing healthcare workforce shortages, improving health disparities, and promoting policy initiatives that support rural healthcare will be critical to ensuring equitable access to healthcare in Montana. By leveraging technology, promoting community-based programs, and addressing the unique needs of rural communities, Montana can work towards improving healthcare access and promoting health equity for all its residents.



